Driven by technological advancements, digital or e-commerce transactions have surged worldwide, requiring efficient regulation for smooth and effective processing. Considering such a surge in the economy, IRBM has described specific guidelines for all e-commerce transactions to ensure the smooth working of businesses without any confusion or lack of knowledge.
This article will provide a detailed understanding of the processing of e-commerce transactions under Malaysia e-Invoicing.
What are e-commerce Transactions under Malaysia’s guidelines?
Sale or Purchase of goods or services through a specific network or platform designed for receiving or placing orders that may not require online payment or delivery of such goods or services are called e-commerce transactions.
eCommerce Transactions can occur among various parties, such as individuals, governments, households, enterprises, or other private or public organizations.
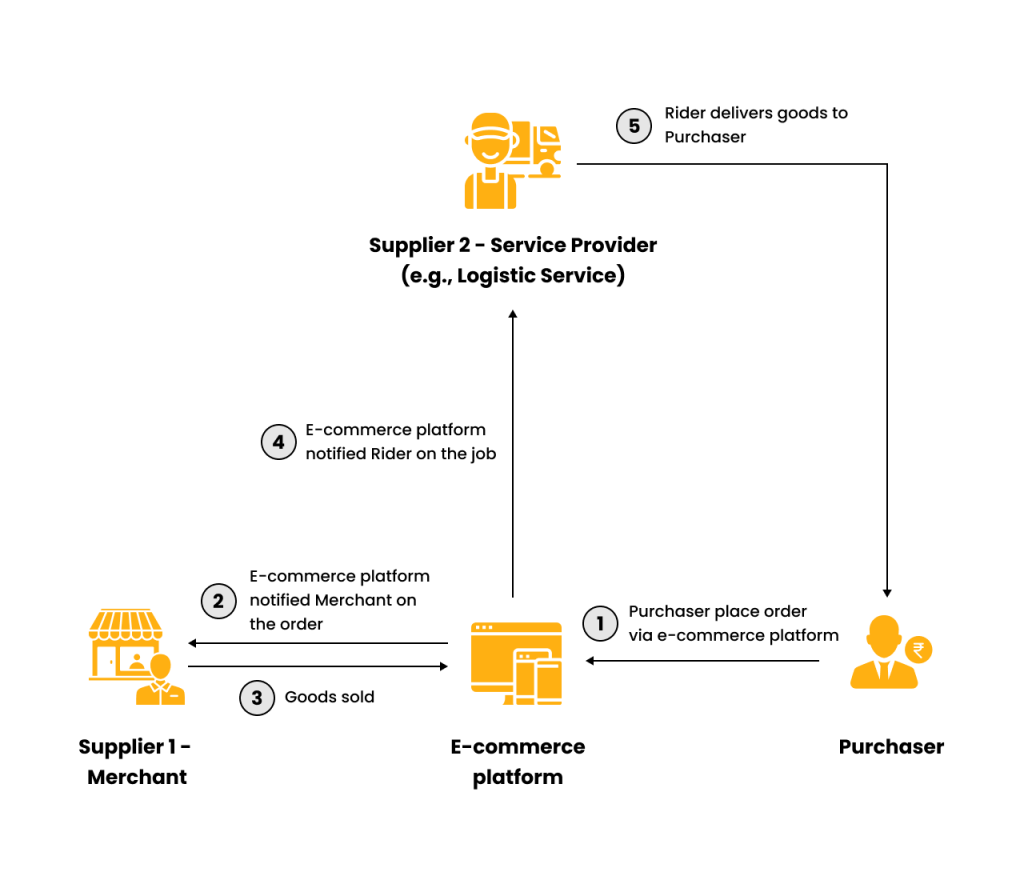
Issuance of e-invoice under various e-commerce transactions
- Issuance of e-invoice by e-commerce platform providers to purchasers
- For e-invoice issuance to Purchaser, the roles of both parties would be as follows:
(a) Supplier: e-commerce platform provider
(b) Buyer: Purchaser
- As per e-invoice guidelines, the e-commerce platform provider will act as a supplier and issue an e-invoice (on the purchaser’s request) or receipt (if no e-invoice is requested) to the purchaser.
- This means the merchant or service provider is not required to issue any invoice/bill/receipt to purchasers for goods sold or services performed.
- If the purchaser does not require an e-invoice, the e-commerce platform provider can aggregate transactions, issue consolidated e-invoices monthly, and submit them to IRBM within seven calendar days after the month’s end.
- Issuance of self-billed e-invoice by the e-commerce platform provider to Merchant and/or Service Provider
- For self-billed e-invoice issuance, the roles of both parties would be as follows:
(a) Supplier: Merchant and/or Service Provider
(b) Buyer: E-commerce platform provider (assumes the role of Supplier to issue a self-billed e-Invoice)
- The Merchant and/or Service Provider is liable to receive payment from the e-commerce platform provider regarding the goods or services sold on the platform. For this, the e-commerce platform provider will issue a self-billed e-invoice to the merchant and/or service provider.
- Self-billed e-invoices can be submitted to IRBM for validation based on the issuance frequency of statements (e.g., daily, weekly, monthly, bi-monthly) issued to the merchant and/or service provider.
- The self-billed e-invoice issuance workflow is similar to that of a normal e-invoice.
- Issuance of e-Invoice from e-commerce platform provider to Merchant and/or Service Provider
- For e-invoice issuance, the roles of the parties would be as follows:
(a) Supplier: e-commerce platform provider
(b) Buyer: Merchant and/or Service Provider.
- The e-commerce platform provider is responsible for issuing an e-invoice for the charges imposed on the merchant and/or service provider for using the platform. The e-commerce platform provider will issue an e-invoice to the merchant and/or service provider for charges imposed.

IRBM issued general and specific guidelines for issuing e-invoices, self-billed e-invoices, and consolidated e-invoices, including Appendix 1 and 2 for the information required to be filled out.
IRBM has provided specific guidelines for more such transactions. Stay connected to gain a detailed understanding of them.








