A brief overview of KSA e-invoicing
E-invoicing was introduced by ZATCA (Zakat, Tax, and Customs Authority- the governing tax authority) in Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) to promote digitization and aim to convert the issue of paper-based invoices to electronic invoices to provide ease of doing business with efficiency and security. This process aims to bring businesses transparency, uniformity, and standardization.
The project has been rolled out in two Phases:
- KSA e-invoicing phase-1 (Generation Phase), which was enforced from 4th December 2021, where all the taxpayers (excluding non-resident taxpayers) and any other parties issuing tax invoices on behalf of suppliers subject to VAT were required to generate and store invoices in electronic format through a compliant electronic solution and including additional fields depending on the type of the transaction.
- KSA e-invoicing Phase-2(Integration Phase), which is enforced from 1st January 2023 in a phased manner, where e-invoicing software or systems of the taxpayers are integrated with ZATCA to make the invoices interoperable between the government and taxpayers’ system to share invoice data.
- KSA e-invoicing Phase-2 requires taxpayers to report the tax invoices to ZATCA in real time for verification. Once ZATCA verifies the invoice, it will be eligible to be shared with the customers.
- However, in the case of simplified invoices, the invoices can be reported to ZATCA for verification within 24 hours of their generation.
- The KSA e-invoicing phase-2 is rolled out in a phased manner. In total, nine waves are implemented with different deadlines for compliance of each wave for the taxpayers registered under VAT in the kingdom, based on the turnover in the calendar year 2021 or 2022 as required. The detailed table for all the e-invoicing requirements and phase-2 wave deadlines are as follows:
Requirements of KSA e-invoicing phase-2
KSA e-invoicing Phase-2, along with integrating taxpayers’ solutions and reporting invoices to tax authorities, also requires other features or information. The requirement is based on the type of invoices issued, i.e., Standard tax invoices or simplified tax invoices. Before we dive into the requirements, let’s briefly discuss the types of invoices.
A tax invoice may be issued in physical format or through electronic transmission of an electronic invoice or e-invoice. However, Paper invoices converted into electronic formats by copying, scanning, or any other mode cannot be considered e-invoices. Therefore, if generated electronically, the standard or simplified tax invoice can be considered an e-invoice.
Standard Tax Invoices- Standard tax invoices are generally for B2B transactions, which contain all the details and mandatory fields of tax invoices as required by the ZATCA.
Simplified Tax Invoices- Simplified tax invoices are generally issued for B2C transactions where buyers’ details are not provided but contain the minimum field required by the ZATCA. Said invoice can also be issued for B2B transactions having a value of supply less than SAR 1000.
Now, let’s dive into the requirements of the government to be implemented in e-invoicing phase-2 by the taxpayers.
The requirements of Phase 2 for the standard and simplified e-invoices are as follows:
| Invoice Generation Requirements | ||
| Requirements | Standard tax invoice | Simplified Tax Invoice |
| Means of Invoices generation | Electronic | |
| Invoice Format (Input) | XML Format | |
| Invoice Format (Output) | Invoice Format of PDF A/3 (XML embedded) | |
| Invoice Field | Generate additional fields required for integration and compliance features. | |
| Invoice Storage | As per VAT regulations and can be accessible by authority at any given time. | |
| Security and Integrity | ||
| Requirements | Standard tax invoice | Simplified Tax Invoice |
| Device Registration | Compliant solutions must be registered on the FATOORA Portal following the onboarding process. | |
| UUID | To be part of e-invoice | |
| Hash | To be part of e-invoice | |
| QR Code | The taxpayer’s solutions will generate the QR code value, and the FATOORA Portal will update the code during the Clearance process. The QR code will then be printed to be visualized on the human-readable invoice by the taxpayer. | Mandated- to be included by the taxpayer. |
| Cryptographic Stamp | Will be applied by the FATOORA portal | Mandated- to be included by the taxpayer |
| Connectivity | The solution should have features of an internet connection for the upload and clearance of invoices. | The solution should have the feature of an internet connection for invoice reporting. |
| Integration | ||
| Requirements | Standard tax invoice | Simplified Tax Invoice |
| Invoice Clearance | Upload and clear invoices via API on a real-time basis on the FATOORA portal. | – |
| Invoice reporting | – | Report the invoice via API on the FATOORA portal within 24 hours of generation. |
Waves deadlines under KSA e-invoicing Phase-2
| Waves under Phase-2 | Turnover Limit | FY in which the mentioned Turnover limit is required to be fulfilled | Compliance Timeline |
| Wave – 1 | More than SAR 3 billion | 2021 | 1st January 2023 |
| Wave -2 | More than SAR 500 million and less than SAR 3 billion | 2021 | 1st July 2023 |
| Wave – 3 | More than SAR 250 million and less than SAR 500 million | 2021 or 2022 | 1st October 2023 |
| Wave – 4 | More than SAR 150 million and less than SAR 250 million | 2021 or 2022 | 1st November 2023 |
| Wave – 5 | More than SAR 100 million and less than SAR 150 million | 2021 or 2022 | 1st December 2023 |
| Wave – 6 | More than SAR 70 million and less than SAR 100 million | 2021 or 2022 | 1st January 2024 |
| Wave – 7 | More than SAR 50 million and less than SAR 70 million | 2021 or 2022 | 1st February 2024 |
| Wave – 8 | More than SAR 40 million and less than SAR 50 million | 2021 or 2022 | 1st March 2024 |
| Wave – 9 | More than SAR 30 million and less than SAR 30 million | 2021 or 2022 | Starting, 1st June 2024 |
All eligible taxpayers will be informed by ZATCA at least six months in advance to implement e-invoicing compliance requirements based on their turnover limit from the date as applicable.
Process of generation and reporting of invoices under KSA e-invoicing Phase-2
The process of generation and reporting of invoices under phase 2 is different for standard tax invoices and simplified tax invoices. Let’s have a look at the process chart and detailed steps to follow:
1. Standard Tax Invoices
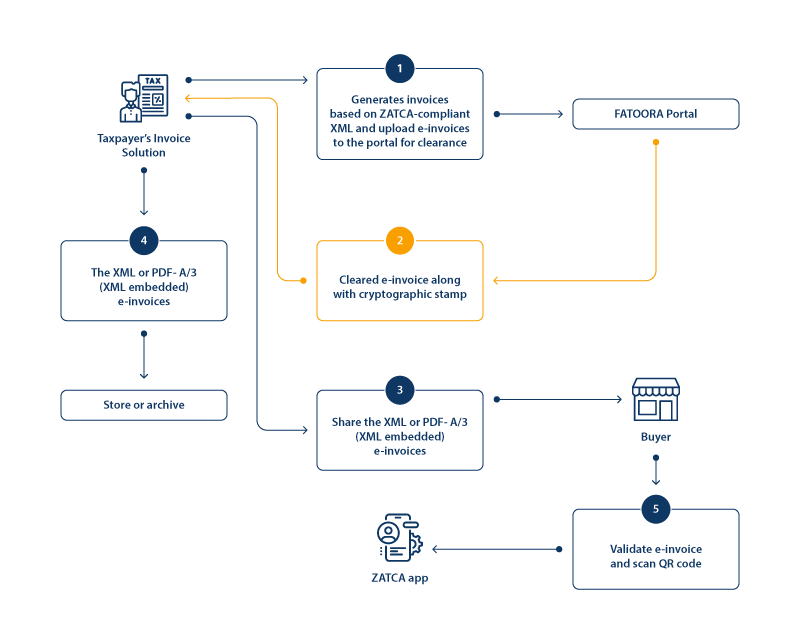
Detailed steps of the process standard tax invoice
- Taxpayers can generate e-invoices in ZATCA-compliant XML format with the required fields in their registered and integrated e-invoicing solution.
- The e-invoices shall be uploaded on the FATOORA portal for clearance.
- The cleared invoices and the cryptographic stamp will be returned to the taxpayer.
- The cleared e-invoices are shared with the buyer in XML or PDF A/3 (XML embedded) format, which can be validated by the buyer using the ZATCA application.
- The e-invoice can be stored/archived in a ZATCA-compliant format that can be easily accessible by the authority.
2. Simplified Tax Invoices
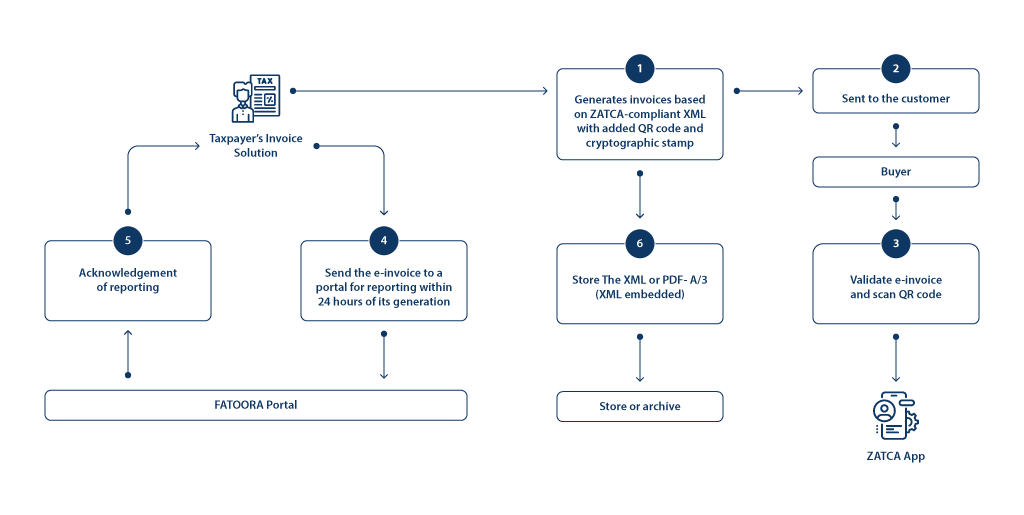
Detailed steps of the process simplified tax invoice
- Taxpayers can generate e-invoices in ZATCA-compliant XML format with the required fields, a QR code, and a cryptographic stamp in their registered and integrated e-invoicing solution.
- The e-invoices are shared with the buyer in XML or PDF A/3 (XML embedded) format, which can be validated by the buyer using the ZATCA application.
- The e-invoices shall be uploaded on the FATOORA portal for reporting within 24 hours of generating the e-invoice.
- The acknowledgment is received from the FATOORA portal on successful e-invoice reporting.
- The e-invoice can be stored/archived in a ZATCA-compliant format that can be easily accessible by the authority.
Prohibited functions of Taxpayer’s e-invoicing Solution
- A person subject to e-invoicing regulations cannot access the e-invoicing system without logging in with a unique ID and password or biometric.
- Default password is not allowed. Password reset in first use will be required for the system.
- The system must log all the activities of e-invoice generation, starting from login authentication.
- No modification allowed in system-generated logs related to the system’s activities.
- All the logged activities should be time stamped and linked by placing the hash of the previous invoice in the associated field of the next invoice in a sequence to prevent their order change.
- No e-invoices can be deleted or cancelled once generated. Any change or cancelation can be done only by issuing a credit note or re-issuing a new invoice.
- The time and date of the system should not be allowed to change in a way that provides false information in the invoice generated.
- The e-invoice solution should not have a feature where invoicing counting can be reset.
- The e-Invoice Solution unit must not generate more than one sequence so that all invoices generated by an e-Invoice Solution Unit are linked using the “Previous Invoice Hash” value into a single chain.
- The solution must not allow software time changes that will change or modify the timestamp value during an e-invoice or Credit/Debit Note issuance.
- The solution must not provide an option to export the cryptographic stamp private stamping key.
In Conclusion
KSA has embarked on a transformative journey in the realm of e-invoicing, aiming to streamline financial processes, enhance transparency, and bolster overall business efficiency. The introduction of e-invoicing requirements underscores the government’s commitment to embracing digitalization and fostering a modern, tech-driven economy.
As businesses navigate the complexities of implementation, they must be compliant for Phase 2 of KSA e-invoicing with ZATCA-qualified solutions. Embracing these changes ensures compliance and opens avenues for improved financial management and strategic decision-making. The transition to e-invoicing in KSA signifies a pivotal step towards a more agile and digitally integrated business landscape poised for sustained growth in the global marketplace.










