In the intricate web of financial reporting, every little piece of data matters. Among the multitude of documents that contribute to accurate and transparent financial reporting, purchase invoices stand out as a critical cornerstone. These seemingly routine documents hold the power to not only validate transactions but also unveil insights that can influence strategic decision-making.
In this blog, we will be delving into the vital role of purchase invoices in financial reporting, exploring their significance and discussing their components, whilst also reviewing the processing of a purchase invoice, and further discovering the technological advancements that are reshaping today’s business landscape.
Understanding Purchase Invoices
But first, we must understand what the invoice in question is. A purchase invoice is a legally binding document issued by a supplier to a buyer during a sale. This document outlines the details of a transaction, including the goods or services purchased, the quantities, its prices, the GST tax amounts, their terms of payment, and other relevant information. It serves as proof of the purchase and establishes the buyer’s liability to pay the supplier. In financial reporting, purchase invoices play a pivotal role in recording expenses accurately and maintaining the integrity of financial statements.
Significance in Financial Reporting
Expense Recognition and Accruals: Purchase invoices facilitate the accurate recognition of expenses in the financial statements. They provide evidence of a liability incurred by the company, and the accrual basis of accounting necessitates recording expenses when incurred, not when cash changes hands. This means that even before the payment is made, the expense needs to be recognized based on the purchase invoice.
Matching Principle: The matching principle dictates that expenses should be matched with the revenues they help generate. Purchase invoices enable this matching by associating costs with the specific revenue-generating activities they support. This principle enhances the accuracy of profit measurement and ensures that financial statements reflect the true economic performance of the company.
Transparency and Auditing: Transparent financial reporting is fundamental for maintaining the trust of stakeholders. Purchase invoices provide auditors with verifiable evidence of transactions and expenses. Auditors can trace the invoices to related financial transactions, validating the accuracy and completeness of the reported figures.
Management Decisions: Purchase invoices provide valuable insights into spending patterns, vendor relationships, and cost structures. By analyzing these invoices, management can make informed decisions regarding cost reduction strategies, negotiation tactics with suppliers, and overall budgeting.
Components of a Purchase Invoice
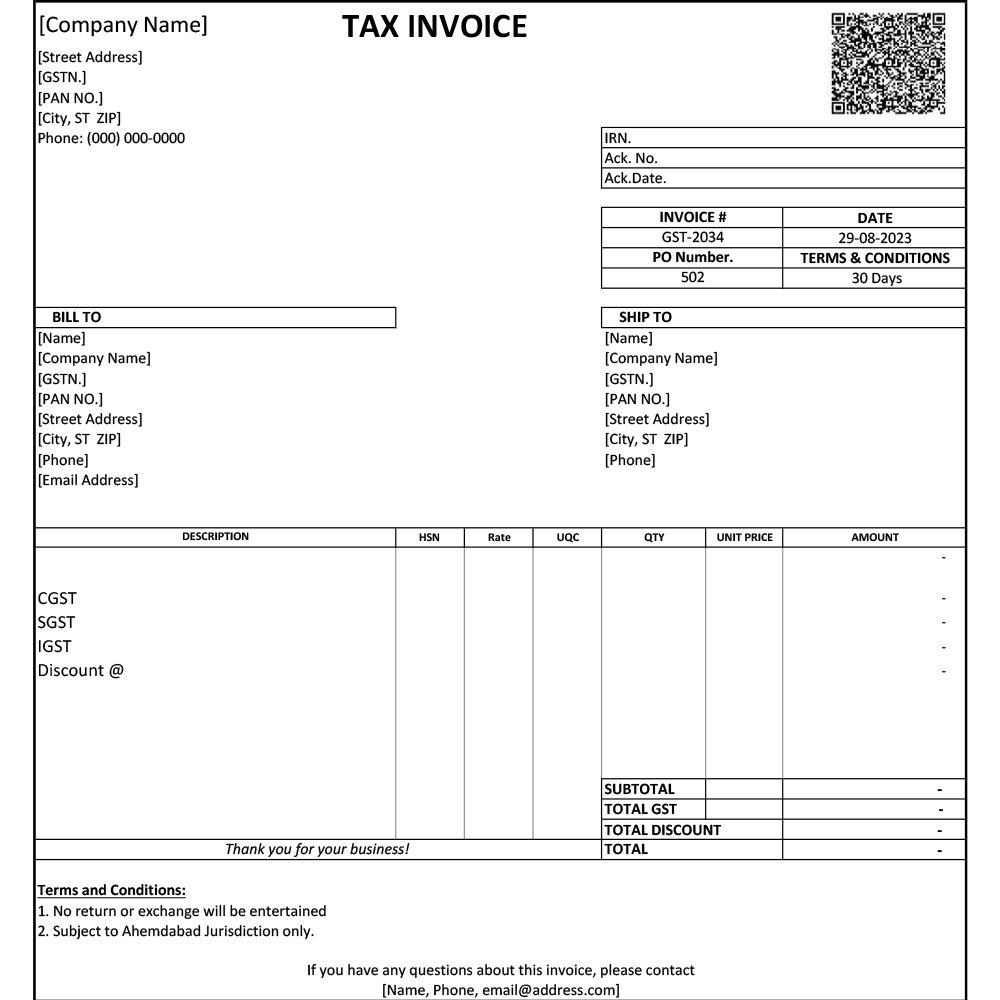
Header Information: This includes the supplier’s name, address, and contact details, and the same details for the buyer.
Invoice Number and Date: A unique invoice number, known as an Invoice Registration Number (IRN), and the date of issuance are crucial for tracking and organization.
Description of Products/Services: A detailed list of items or services purchased with HSN (Harmonized System of Nomenclature) codes, including total quantities, unit prices, and any applicable discounts.
Total Amount: The total amount due, including the subtotal, taxes, and any additional charges.
Payment Terms: The agreed-upon terms of payment, such as the due date, payment method, and any early payment discounts as well as late payment charges.
Purchase Order (PO) Reference: If the purchase was made based on a purchase order, the PO number is referenced to link the invoice to the initial order.
Terms and Conditions: Any additional terms and conditions regarding the sale that are agreed upon between the buyer and the supplier.
Processing Purchase Invoices
Traditionally, processing purchase invoices has been a manual and time-consuming task, highly prone to human errors and inefficiencies. However, with the advent of technology, automation is transforming this landscape. Automated invoice processing involves:
Scanning and Data Extraction: Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technology scans the paper or digital invoices, extracting relevant data such as invoice numbers, amounts, and line items.
Validation and Matching: Automated systems compare the extracted data with other the documents provided, like purchase orders and receiving reports to ensure the accuracy and authenticity of data on the invoice.
Workflow and Approval: Invoices are automatically routed through approval workflows, streamlining the process, and reducing delays in making and processing payments.
Integration with Accounting Systems: Data from validated invoices seamlessly flows into the accounting software, reducing manual data entry errors from traditional invoicing methods and improving data consistency.
Technological Advancements
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are enhancing invoice processing by improving data extraction accuracy and enabling systems to learn from historical data, making them better at data validation and exception handling over time.
Blockchain Technology: Blockchain ensures the immutability and transparency of transactions, making it an ideal solution to accurately authenticate and trace invoices.
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI): EDI allows for seamless, rapid, and standardized electronic interaction between trading partners, expediting the exchange and transfer of invoices and other business documents.
In closing, purchase invoices might just seem like mundane documents, however their role in financial reporting is anything but ordinary. They form the very foundation for accurate expense recognition, uphold the matching principle, provide transparency for auditing, and guide strategic decision-making in a firm.
As technology continues to reshape financial processes, automated invoice processing is becoming the norm, revolutionizing efficiency, and accuracy around the world. Embracing such technological advancements can help organizations elevate their financial reporting practices, ensuring compliance of tax laws and regulations, maintain transparency, and make better-informed decisions over the long term.










