To simplify e-invoicing in Malaysia, IRBM has analyzed all possible transactions/cases and provided detailed explanations of the e-invoice workflow. Disbursement and reimbursement among trading parties are such transactions detailed by IRBM. This article breaks down both terms, explains their e-invoice treatment, and clarifies how to differentiate between disbursement vs reimbursement e-invoice cases all of which are supported by a comprehensive Malaysia e-invoicing solution designed for compliance with IRBM guidelines.
Disbursement
The out-of-box expense incurred by the payer (buyer) but paid by the payee (seller) to the third party on behalf of the payer for the sale of goods or services rendered by the payee to the payer.
Characteristics of Disbursement
Reimbursement
- The expense legally belongs to the buyer, not the seller.
- The seller only makes payment on behalf of the buyer.
- The seller cannot mark up or profit from this payment.
- It is not a claimable expense Malaysia for the seller.
- Such amounts are excluded from taxable income under disbursement vs reimbursement accounting.
Example of Disbursement
A law firm pays a government filing fee of RM 500 on behalf of a client. The invoice is issued by the government agency directly to the client. The law firm pays the fee, provides proof of payment, and recovers the exact amount from the client without charging GST.
Reimbursement
The out-of-box expense incurred by the payee (seller) during the sale of goods or rendering of services on behalf of the payer (buyer), which will later be reimbursed from the payer.
Characteristics of Reimbursement
The expense is incurred by the seller while performing a service.
- The seller later recovers the expense from the buyer.
- The seller may treat this as part of its income and claim input tax where applicable.
- These are claimable expenses Malaysia for tax computation.
Example of Reimbursement
A marketing agency books an event hall for RM 2,000 while managing a client’s campaign. The invoice is issued to the agency, not the client. Later, the agency bills the client RM 2,000 for the hall as reimbursement, together with its professional fee.
This transaction is classified as a reimbursement under e-invoice reimbursement and disbursement guidelines.
Detailed Understanding of Different Scenarios
To help you understand the scenarios more accurately, the following terms represent the buyer, seller, and third party.
- The first supplier (seller) represents Supplier-1
- The third party represents Supplier-2
Scenario-1: Supplier -1 (Seller) issuing e-invoice to buyer
It is the case where Supplier-2 has paid supplier-1 on behalf of the buyer for the sale of goods or the rendering of services to the buyer based on the contract between the buyer and supplier-2.
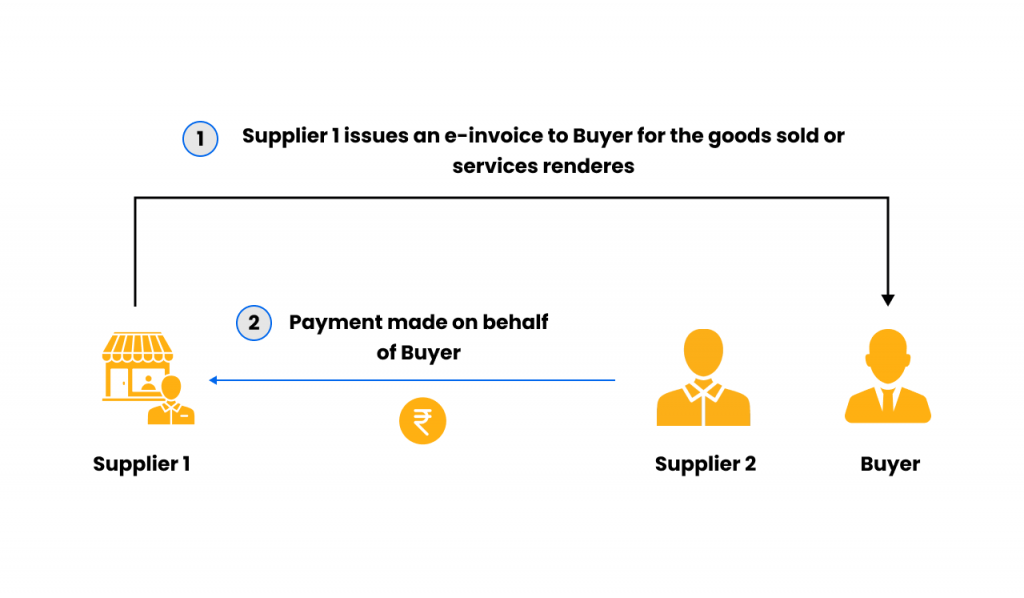
The steps to issue an e-invoice in this scenario are as follows:
- Buyer and supplier-2 have entered into an agreement to sell goods or render services.
- As part of this agreement, supplier-2 pays supplier-1 on behalf of the buyer for an additional supply of goods or services to the buyer.
- However, supplier-1 will issue an e-invoice directly to the buyer.
- Supplier-2 will make payment to supplier-1 and claim payment proof from supplier-1
- Supplier-2 will issue an e-invoice to the buyer for the sale of goods or services rendered by supplier-2. It will not include the amount paid by supplier-2 to supplier-1, and supplier-2 cannot even issue an additional e-invoice.
- Supplier-2 shall provide the buyer with proof of payment so that the buyer can be reimbursed for the money paid to supplier-1.
Let’s understand this with a simple example:
- ABC agrees with XYZ to render event planning services for RM 50000.
- ABC approaches a decoration company to supply decorative items for RM 10000.
- The decoration company will issue an e-invoice in the name of XYZ, for which ABC will make the payment and provide payment proof of RM 10000.
- Now, ABC will issue an e-invoice to XYZ for its event planning service of RM 50000, which shall not include the amount paid to the decoration company nor issue another invoice.
- ABC shall provide the payment proof of RM 10000 issued by ABC to XYZ to get reimbursement.
Scenario-2: Supplier-1 issued e-invoice to supplier-2
Supplier-1 issues an e-invoice in the name of supplier-2 for the sale of goods or services intended for use by the buyer, and supplier-2 makes the payment according to the agreement between the buyer and supplier-2, which will eventually be recovered from the buyer.
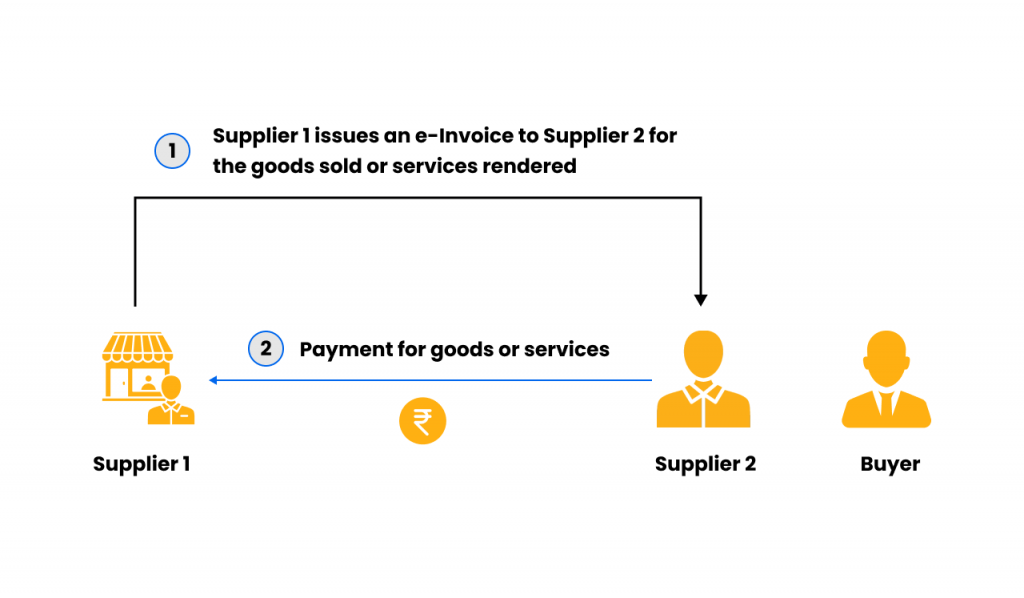
The steps to issue an e-invoice in this scenario are as follows:
- Supplier-2 and buyer enter into a contract for the sale of goods or services rendered. During this contract, supplier-2 shall pay any expense incurred on behalf of the buyer.
- Supplier-1 will issue an e-invoice to supplier-2, and supplier-2 will pay supplier-1 for the invoice for any additional expenses incurred.
- Supplier-1 will issue proof of payment to supplier-2 for the invoice.
- Supplier-2 will issue an e-invoice to the buyer for the sale of goods or services rendered by him and for the sale of goods or services incurred on behalf of the buyer. Both the suppliers shall be mentioned as separate line items in the invoice.
Let’s continue the example to understand this transaction
- Suppose ABC approaches a catering company to provide catering services for RM 30000 for the event.
- The catering service issues an invoice of RM 30000 to ABC, and ABC pays it and receives proof of payment of RM 30000.
- ABC will now issue an invoice for RM 50000 for their event planning service and catering services of RM 30000. Total invoice of RM 80000. However, the invoice shall show both services as separate line items.
IRBM has provided specific guidelines for more such transactions. Stay connected to gain a detailed understanding of them.
Disbursement vs Reimbursement: Key Differences
| Basis | Disbursement | Reimbursement |
| Ownership of expense | Buyer’s expense | Seller’s expense |
| Tax impact | Not subject to tax | Subject to output tax |
| Claimability | Not claimable expenses Malaysia | May be claimable |
| Income recognition | Not income for seller | Part of seller’s income |
| IRBM e-invoice treatment | Buyer claims directly | Seller includes in e-invoice |
These distinctions form the foundation of reimbursement vs disbursement e-invoice compliance in Malaysia.
E-Invoicing Treatment under IRBM Guidelines
Malaysia e-invoicing IRBM guidelines specify distinct handling for both types of expenses:
When to Issue an e-Invoice for Disbursement
- The third-party (Supplier-1) issues an e-invoice directly to the buyer.
- The intermediary (Supplier-2) provides proof of payment but does not issue an additional e-invoice.
- No GST is levied by Supplier-2 for this amount.
When to Issue an e-Invoice for Reimbursement
- The intermediary (Supplier-2) issues one consolidated e-invoice to the buyer.
- The e-invoice includes both its own service and the reimbursed cost as separate line items.
- Supplier-2 accounts for GST on the entire amount.
Documentation and Proof Requirements
- Copy of the original invoice issued by Supplier-1.
- Proof of payment between all involved parties.
- Contract or agreement showing cost-bearing responsibility.
- Corresponding e-invoice records per Malaysia e-invoicing IRBM guidelines.
Understanding these rules ensures full compliance with e-invoice reimbursement and disbursement standards under Malaysia’s e-invoicing framework.
FAQS
1. What is a disbursement in Malaysia e-invoicing?
A disbursement occurs when the seller pays a third party on behalf of the buyer, and the third-party issues the e-invoice directly to the buyer.
2. What is a reimbursement in e-invoicing?
It’s when a seller incurs a cost while providing goods or services and later recovers it from the buyer through an e-invoice.
3. When is an e-invoice required for disbursement?
The e-invoice is required only from the actual supplier (Supplier-1) to the buyer; intermediaries do not issue additional invoices.
4. What are common mistakes to avoid?
Incorrect classification between disbursement and reimbursement, missing proof, and reporting disbursement values as taxable items.
5. How do Malaysia e-invoicing IRBM guidelines treat claimable expenses?
Only reimbursements may qualify as claimable expenses Malaysia, while disbursements remain pass-through costs excluded from tax.