Organizations must continuously evolve to stay competitive and relevant in today’s fast-paced and ever-changing business landscape. The concept of transformation has become a pivotal driver for businesses seeking to adapt, innovate, and thrive in this dynamic environment. Organizations are strategically gaining a competitive edge by automating legacy processes, upgrading the technology landscape, and optimizing workflows. Transformation extends beyond technology and operations and encompasses cultural change, which is vital in fostering a more agile and customer-centric organization.
The essential elements of transformation include developing a corporate vision story, re-organizing organizational design, developing mission and values, setting objectives and measurement strategies, reviewing the current business/market scenario, and creating the business/marketing plans. For effective transformation, there is a need to pursue the fundamental purpose of the business while giving due consideration to its core values and meeting and reconciling the contemporary needs of the target market and key stakeholders effectively and optimally.
Change vs Transformation: Understanding the Distinctive Paths to Organizational Evolution
Change is predictable as it focuses on executing a pre-defined shift. It involves the execution of several finite initiatives that may or may not affect the entire organization. Discrete change initiatives may succeed without sufficient alignment of resources.
On the other hand, transformation is much more unpredictable and involves higher risk as it involves discovering or inventing a business model with an eye towards the future. It connotes a portfolio of interdependent or intersecting, multi-dimensional initiatives that aim to reinvent the entire organization. Thus, it demands a much broader set of capabilities and more dynamic coordination, collaboration, and communication of resources (human, financial, technical).
Thus, change initiatives may be a part of the transformation process but cannot be the other way around. Thus, the success of a couple of change initiatives may not be the success of the overall transformation process.
Embracing Transformation: Unveiling the Imperative for Organizational Growth and Resilience
For a business to be successful, it needs to adopt new ways of delivering value to its customers and thrive in the rapidly changing competitive landscape and underlying market economics. With rapid industrial and technological changes, the market scenarios are now changing faster than ever. So, the risk of disruption and fear of missing out on growth opportunities is the impetus for the need to transform. Efficiency gains, new business restrictions, and reduced costs also drive transformation.
Types of Transformations
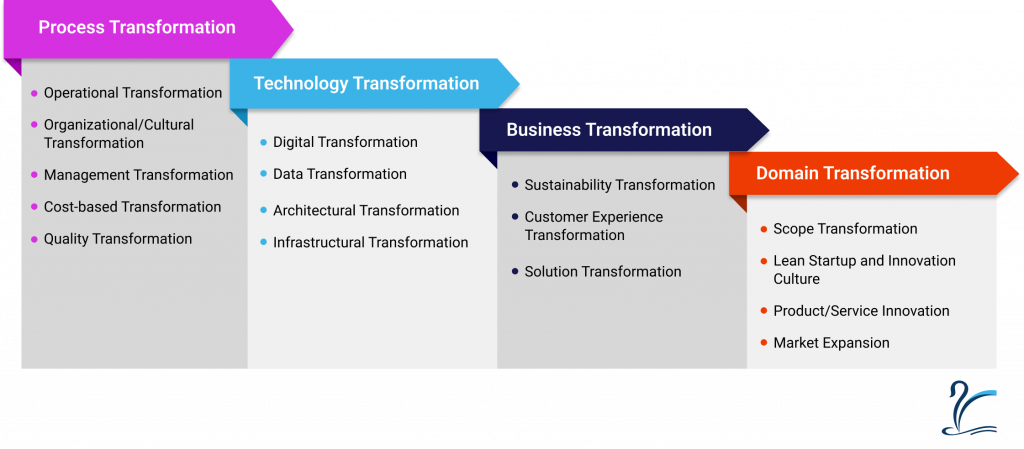
Process Transformation
Business processes form an essential focus of an organization’s activity. Modernizing legacy processes, improving quality, enhancing customer experience, lowering costs, strengthening security, or increasing efficiency and profitability are the motives that urge an organization to opt for transforming the business processes using innovative technologies like data, analytics, APIs, machine learning, robotic process automation (RPA). While transforming the business processes, a business shifts from a function-oriented vertical vision to a business-oriented transversal vision. It fundamentally changes how a business operates and focuses on finite areas of the business. It includes the following types of transformations:
- Operational transformation: It focuses on the gradual overhaul of the organization’s daily operations (processes and procedures). Rather than implementing simultaneous changes in everything, updating a specific department with the latest industry standards and practices and making changes department-wise will allow them to stay competitive.
- Organizational/cultural transformation: Transformation brings with it the need for a bias towards testing, learning, implementing, and then again testing and repeating the process while greatly relying on the business ecosystems. It may implicate changing the hierarchical structure, hiring new staff, improving staff skills with courses and training, inspiring teamwork and collaboration between staff members, or even the complete restructuring of the organization to meet the purpose. Agile workflows and decentralized decision-making demand redefining the mindsets, talents, capabilities, behavior, interactions, attitudes, values, and processes in the organization. Though the transformation success depends on the long-term cultural/organizational transformation, you should regard it as a product rather than a pre-requisite for transformation initiatives. A top-down approach, where the top management adopts the transformation to serve as an example for other staff members, helps implement this transformation.
- Management transformation: With the changing market demands or new managerial needs due to business expansion, an organization may need to improve internal relations and the efficiency of the communication and decision-making process to streamline certain operations. This may involve restructuring, eliminating, or adding managerial roles or certain steps the employees must complete to get management approval for their decisions. Communication, collaboration, and empowerment play a key role here.
- Cost-based transformation: Any expenses a business requires constitute its costs. An organization needs to transform its costs to lower overhead expenses such as rent and payroll, which do not directly contribute to producing a product or service. Also, restructuring the costs may lead to substantial profits by bringing down the cost per unit for one or more of its products or services.
- Quality transformation: A business may go for an internal upgrade of its products, services, or connected operations for reasons such as customer satisfaction, customer engagement, new technology or machinery in the market, or to enhance its USP. This demands changes in personnel skills, enhancing the quality of the prime materials, and improving the technical capabilities of the machinery being used.You must consider all the resources needed for this transformation to implement it successfully.
Technology Transformation
Technology plays a central role in transformation initiatives and is a growth driver. It brings significant changes in how organizations operate and customers consume services. This transformation significantly affects analog companies relying on manual processes that must develop new skill sets and resources to realize the potential of technology-aided innovation. Newer, faster, and more efficient systems can be set in place with technology transformation in an organization that includes:
- Data transformation: It results from the explosion of available data, data sharing options, data analytics, and data storage capacity. It allows businesses to gain deep intelligence into all aspects of the business to inform about areas for improvement and changes the decision-making ability for innovation. Keeping risk management priorities and business value propositions in view while balancing them with the resources needed for data transformation poses the main challenge.
- Digital transformation: Incorporating digital technology in all business areas changes how businesses function and interact with customers to change business performance. It is a team effort that demands tremendous cross-departmental coordination within the organization. Digital transformation includes revamping the digital media strategy of an organization in its marketing and advertising strategy, such as rebranding all digital assets or developing a new email campaign. It helps a business by enhancing data collection, providing data-driven customer insights, strengthening resource management, augmenting customer experience, encouraging a digital culture, and increasing profits, agility, and productivity.
- Architectural transformation: Modern technology can improve the product (application/software) being used by the organization to achieve its business goals. Shifting from the monolith to microservice or event-driven architecture is an example of such transformation. It considers all the features, functional and non-functional requirements, business requirements, and technical capabilities.
- Infrastructural transformation: Replacing legacy systems and infrastructure with modern technology stacks to change how products and services are consumed, such as moving from on-premises to cloud-based models, add to the efficiency of business processes.
Business Transformation
It aims at the fundamental building blocks of profit-building and value delivery in the industry. Several new opportunities for growth can open by changing the basic building blocks of how value is delivered in the industry. This may involve several steps as it involves significant changes in the organization’s industry, customer base, technological landscape, certain operations, products, funds, and revenue sources. These initiatives are often launched separately while the traditional business continues to operate in parallel. This transformation can be related to the following types of transformations:
- Sustainability transformation: For many industries and organizations, the reason for transformation may be to reduce the business processes’ or operations’ impact on the environment. The goal is to deal with these environmental challenges without affecting the organization’s profits.
- Customer experience transformation: Most organizations have a clear customer persona in mind and design their interactions with their customers to attract and retain them. However, if the current techniques being used become obsolete due to some external factors, the organization needs to reinvent ways to create a new customer base and also retain the existing customers. This transformation may include sales CRM, chatbots, automated emails, device compatibility of applications, or any other issues customers highlight in their feedback or other interactions with the organization.
- Solution transformation: It refers to the process of making significant changes to how a company approaches and addresses its business challenges and problems. It involves rethinking and redefining the solutions to tackle specific issues, improve operational efficiency, enhance customer experience, and achieve overall business goals. Solution transformation aims to leverage innovative technologies, processes, and strategies to create more effective and sustainable solutions.
Domain Transformation
In the current market scenario, industry boundaries are becoming blurred. New sets of non-traditional competitors are now created for products and services beyond their traditionally actively served markets. An organization can create new value opportunities by entering a new industry to explore new clients with domain transformation. It is not just about creating a business extension or adjacency but creating a completely different business in a fundamentally different market space. Technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), internet of things (IoT), and augmented reality (AR) are unlocking new business domains. They can be sourced more easily and cost-efficiently now. Domain transformation is related to the following transformation primarily:
- Scope transformation: The scope of the business shifts entirely or expands with the transformation of its domain. This may refer to a change in the geographical areas or product ranges. With this, all the activities that a business performs, ranging from product development, marketing, pre-sales, sales, etc., need to be restructured.
- Lean startup and innovation culture: Encouraging an innovation-driven, lean startup culture can lead to domain transformation, allowing companies to experiment, learn, and adapt their offerings continuously.
- Product/service innovation: Businesses can transform their domain by introducing new and innovative products or services to meet evolving customer needs and stay ahead of the competition.
- Market expansion: A company can undergo domain transformation by expanding its target market or diversifying into new geographic regions or customer segments. It may involve entering international markets, expanding to new cities, or targeting a different demographic.
Understanding Transformations
Transformation is a high-risk, multi-dimensional process, so you should critically plan to align the people, processes, and technology appropriately. Moreover, you don’t need to go for all types of transformation in your organization in one go. You can prioritize your needs and goals and form a digital transformation strategy that focuses on achieving them gradually.
Though change management consultants can aid the transformation process in multiple ways, bringing an organization through the murky waters of transformation demands laying a foundation for continuous improvement. Cygnet Domain and Consulting services help you leverage technological disruption and innovation to lay this foundation for a “future-proof” organization through digital transformation consulting services.










